Dan Rigden. Selected Publications
Back to
top page
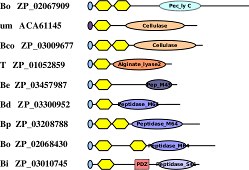 The
BACON domain. By mining metagenomic data from gut bacteria we have
found a novel all-β domain with all the
hallmarks of a carbohydrate-binding module. It's also in many proteases
leading us to suspect that it might often bind to a glycoprotein, perhaps
mucin. The full story is out in
FEBS Lett.
We're proud that this work was based on preliminary data obtained by a
student on our
Masters course in Bioinformatics.
The
BACON domain. By mining metagenomic data from gut bacteria we have
found a novel all-β domain with all the
hallmarks of a carbohydrate-binding module. It's also in many proteases
leading us to suspect that it might often bind to a glycoprotein, perhaps
mucin. The full story is out in
FEBS Lett.
We're proud that this work was based on preliminary data obtained by a
student on our
Masters course in Bioinformatics.
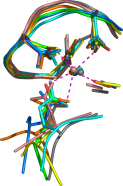 The
DxDxDG calcium-binding motif. This motif appears to have evolved many times
independently. I know of no other example of such striking convergent
evolution. This work was published a little while ago in
J. Mol. Biol.,
but Duncan Woodhead, a PhD student shared with
Prudence Wong
in Computer Science, has
contributed to a significant update that in
PLoS ONE.
The
DxDxDG calcium-binding motif. This motif appears to have evolved many times
independently. I know of no other example of such striking convergent
evolution. This work was published a little while ago in
J. Mol. Biol.,
but Duncan Woodhead, a PhD student shared with
Prudence Wong
in Computer Science, has
contributed to a significant update that in
PLoS ONE.
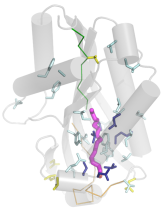 Sometimes
recognising distant homology from non-trivial structure superposition is
informative about function. This example is the
unexpected relationship between Erwinia virulence factor and Bacillus thuringiensis cytolytic
toxins, important weapons for production of transgenic pest-resistant crops.
Recognising the connection and mapping sequence conservation predicts the
location of the lipid binding site in the toxins. This work is now out
in FEBS Lett.
Sometimes
recognising distant homology from non-trivial structure superposition is
informative about function. This example is the
unexpected relationship between Erwinia virulence factor and Bacillus thuringiensis cytolytic
toxins, important weapons for production of transgenic pest-resistant crops.
Recognising the connection and mapping sequence conservation predicts the
location of the lipid binding site in the toxins. This work is now out
in FEBS Lett.
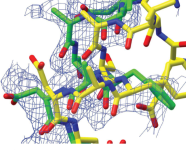 Molecular
Replacement with ab initio models. This BBSRC-funded project has
resulted in a program called AMPLE, now released in the CCP4 suite. You
can read about it in the CCP4 newsletter
here or get a full description at
Acta Cryst
D. They kindly let me put the pdf and
supplementary here
too.
Molecular
Replacement with ab initio models. This BBSRC-funded project has
resulted in a program called AMPLE, now released in the CCP4 suite. You
can read about it in the CCP4 newsletter
here or get a full description at
Acta Cryst
D. They kindly let me put the pdf and
supplementary here
too.
 Pex13
is an essential factor for import of proteins into the peroxisome. The
trypanosomatid Pex13 could not be identified by standard BLAST searches.
It's eventual identification rested on the presence of short YG-containing
repeats which turn out to be the only conserved factor between Pex13 proteins of
different species. This is out in
Biochim. Biophys. Acta.
Pex13
is an essential factor for import of proteins into the peroxisome. The
trypanosomatid Pex13 could not be identified by standard BLAST searches.
It's eventual identification rested on the presence of short YG-containing
repeats which turn out to be the only conserved factor between Pex13 proteins of
different species. This is out in
Biochim. Biophys. Acta.
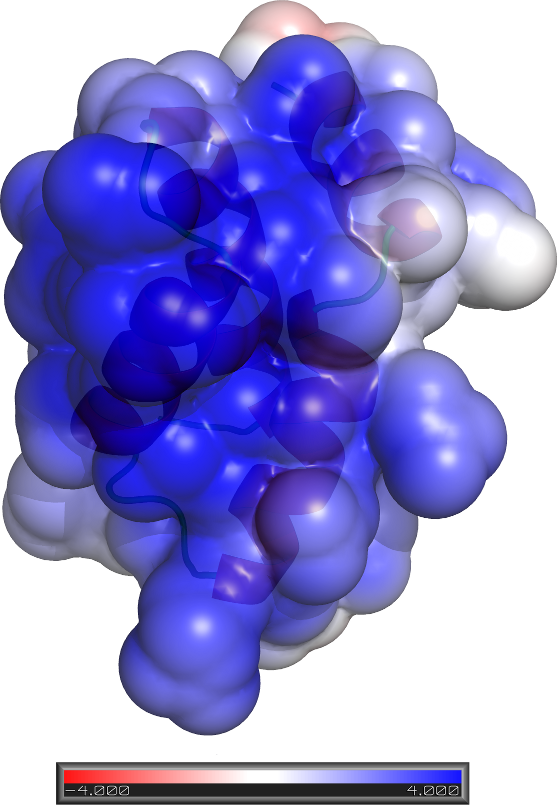 Pfam
contains many Domains of Unknown Function (DUFs). By combining ab
initio modelling with profile-profile matching and non-homology methods, we
proposed that many DUFs, encompassing thousands of sequences, act as DNA-binding
proteins. This work is out in
OMICS: A
Journal of Integrative Biology.
Pfam
contains many Domains of Unknown Function (DUFs). By combining ab
initio modelling with profile-profile matching and non-homology methods, we
proposed that many DUFs, encompassing thousands of sequences, act as DNA-binding
proteins. This work is out in
OMICS: A
Journal of Integrative Biology.
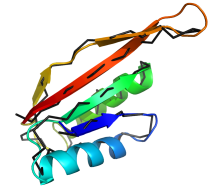 Function
annotation of SpoVS. This protein was characterised as being somehow
involved in bacterial sporulation. Both comparative and ab initio
modelling confirmed an Alba-like fold for SpoVS, predicting it to function in
controlling gene expression patterns during sporulation. The full story
and GerM analysis were published in
Bioinformatics.
Function
annotation of SpoVS. This protein was characterised as being somehow
involved in bacterial sporulation. Both comparative and ab initio
modelling confirmed an Alba-like fold for SpoVS, predicting it to function in
controlling gene expression patterns during sporulation. The full story
and GerM analysis were published in
Bioinformatics.
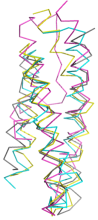 Novel
MIT domains. Even the most sensitive PSI-BLAST techniques leave a grey
area in searches for the short, sequence diverse MIT domain. We have found
profile-profile matching coupled with ab initio
modelling to be highly effective in picking out true MIT
domains from among contaminants such as, in this case, the TPR repeat.
More, including experimental validation of one example, in our
FEBS Lett.
article.
Novel
MIT domains. Even the most sensitive PSI-BLAST techniques leave a grey
area in searches for the short, sequence diverse MIT domain. We have found
profile-profile matching coupled with ab initio
modelling to be highly effective in picking out true MIT
domains from among contaminants such as, in this case, the TPR repeat.
More, including experimental validation of one example, in our
FEBS Lett.
article.
Back to
top page
The contributions of valued collaborators on most of the above are gratefully
acknowledged.
Please e-mail me if you can't access
these articles from where you are and would like a reprint.
 The
BACON domain. By mining metagenomic data from gut bacteria we have
found a novel all-β domain with all the
hallmarks of a carbohydrate-binding module. It's also in many proteases
leading us to suspect that it might often bind to a glycoprotein, perhaps
mucin. The full story is out in
FEBS Lett.
We're proud that this work was based on preliminary data obtained by a
student on our
Masters course in Bioinformatics.
The
BACON domain. By mining metagenomic data from gut bacteria we have
found a novel all-β domain with all the
hallmarks of a carbohydrate-binding module. It's also in many proteases
leading us to suspect that it might often bind to a glycoprotein, perhaps
mucin. The full story is out in
FEBS Lett.
We're proud that this work was based on preliminary data obtained by a
student on our
Masters course in Bioinformatics. 



